| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | Homeodomain ligand |
| Functional site description: | The YPWM motif in HOX proteins confers binding to PBX homeobox domains. |
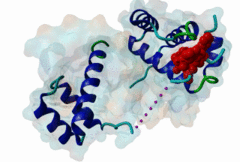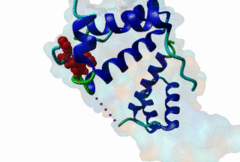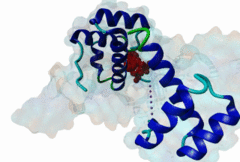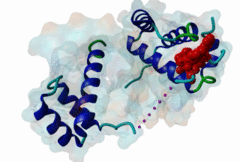
| ELM Description: | The Homeobox (Hox) family consists of a large number of transcription factors which have a vital role in development of the embryo in determining the anterior/posterior and rosto/caudal axis in multicellular organisms. Hox proteins share a conserved 60 amino-acid region; homeodomain, which has specific DNA binding activity, and promotes regulation of multiple target genes (Gehring,1994). The YPWM functional site, is found in several Hox proteins and is located N-terminal in respect to the homeodomain (Qian,1992), and acts as a ligand to the extended Pbx homeodomain, forming a hetrodimer. This interaction increases the DNA binding affinity of the Hox proteins containing the YPWM functional site. Structural data (1LFU; Sprules,2003) suggest a lock and key mechanism where the YPWM motif engages in an interaction in a hydrophobic pocket located in the extended Pbx homeodomain. |
| Pattern: | [FY][DEP]WM |
| Pattern Probability: | 9.953e-07 |
| Present in taxon: | Metazoa |
| Interaction Domain: |
Homeobox (PF00046)
Homeobox domain
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
The YPWM motif in HOX proteins confers binding to PBX homeodomains. |
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement