LIG_BRCT_MDC1_1
| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | BRCT phosphopeptide ligands |
| Functional site description: | BRCT domains are protein modules mainly found in Eukaryota. BRCT domains are present in proteins that are associated with DNA damage response. They recognize and bind specific phosphorylated serine (pS) sequences. This phospho-protein mediated interaction of the BRCT domain has a central role in cell-cycle check point and DNA repair functions. |
| ELMs with same func. site: | LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_1 LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_2 LIG_BRCT_MDC1_1 |
| ELM Description: | The LIG_BRCT_MDC1_1 motif found in Metazoa. The tandem BRCT repeats of MDC1 directly bind to the phosphorylated tail of H2AX (S..Y$), in a manner that is specific to the Carboxy-terminal Tyr residue. By homology, the equivalent motif may be S..F$ in Viridiplantae or S..L$ in Fungi but direct experimental evidence is lacking. |
| Pattern: | .(S)..Y$ |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0000026 |
| Present in taxon: | Metazoa |
| Interaction Domain: |
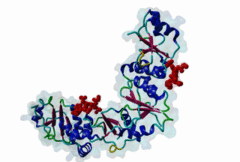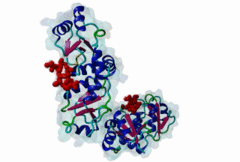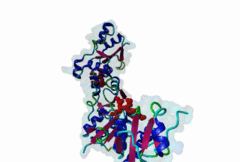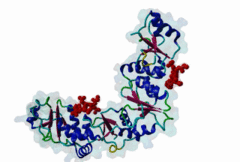
BRCT (PF00533)
BRCA1 C Terminus (BRCT) domain
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
BRCT domains were first identified in and named after the breast cancer susceptibility protein BRCA1 (Zhang,1999). They have alpha/beta structures that occur singly or as multiple repeats. BRCT domains are 80-100 amino acid in length and function as phosphopeptide ligands (Clapperton,2004). They are found in nuclear proteins that are typically associated with cell cycle checkpoint functions responsive to DNA damage (Glover,2004). An unusual feature of paired BRCT motifs is that the phosphopeptides bind across the domain-domain interface (Clapperton,2004). Available data when this entry was prepared suggest that BRCTs may bind exclusively to phosphoserine peptides. By contrast FHA domains, which are often found in a similar functional context, recognise phosphothreonine peptides (LIG_FHA_1). Many of the BRCT ligands are likely to be at pSQ motifs phosphorylated by the checkpoint kinases, ATM, ATR, DNA-PK (Glover,2004). BRCA1-binding motifs are S..F.K (high affinity) or S..F (lower affinity) (Clapperton,2004). Metazoa MDC1 binds histone H2AX C-terminal S..Y$ motifs (Lee,2005), which may be S..F$ in plants and S..L$ in Fungi, but experimental evidence has been lacking. Also, a poorly characterised motif binding the TopBP1 BRCT may match the pattern S.II but more data is needed (Liu,2003). Since consensus motifs have so far been defined for just a few BRCT domains, the range of different binding motif patterns could be quite large. |
-
Complicated tails: histone modifications and the DNA damage response.
Vidanes GM, Bonilla CY, Toczyski DP
Cell 2005 Jul 1; 121 (7), 973-6
PMID: 15989948
-
Structure of the BRCT repeat domain of MDC1 and its specificity for the
free COOH-terminal end of the gamma-H2AX histone tail.
Lee MS, Edwards RA, Thede GL, Glover JN
J Biol Chem 2005 Sep 16; 280 (37), 32053-6
PMID: 16049003
-
MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated histone H2AX to regulate cellular
responses to DNA double-strand breaks.
Stucki M, Clapperton JA, Mohammad D, Yaffe MB, Smerdon SJ, Jackson SP
Cell 2005 Dec 29; 123 (7), 1213-26
PMID: 16377563
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
| Acc., Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | #Ev. | Organism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P16104 H2AFX H2AX_HUMAN |
139 | 143 | TVGPKAPSGGKKATQASQEY | TP | 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) |
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement