| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | UHM domain Ligand Motif |
| Functional site description: | The UHM Ligand Motifs (ULMs) are short induced fit modules with a linear motif signature that mediate dynamic interactions between some splicing factors. UHMs are variants of the large RRM domain family that have swapped RNA-binding for peptide-binding as the primary function. |
| ELM Description: | SF1 has a single ULM while SAP155 has several ULMs that can bind U2AF65. An idealised motif would be something like KRKRSRWD. However the length of the positively charged run is variable, the Ser - when present - may be regulating association by phosphorylation and the Asp, though clearly contributing to interactions in solved ULM complexes, is not conserved in the SF1 motif. These considerations were taken into account in defining the pattern. |
| Pattern: | [KR]{1,4}[KR].[KR]W. |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0000153 |
| Present in taxon: | Eukaryota |
| Interaction Domain: |
RRM_1 (PF00076)
RNA recognition motif. (a.k.a. RRM, RBD, or RNP domain)
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
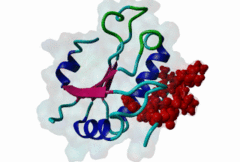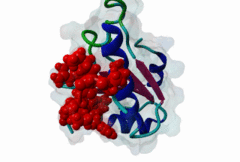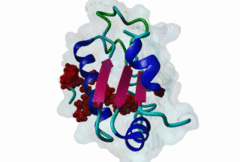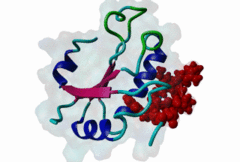
An unusal subgroup of RRM domains (PF00076) termed UHMs (U2AF Homology Motifs) have been found to have no (or weak) RNA-binding activity (Kielkopf,2004). Instead of RNA, UHMs appear to bind to short induced fit protein elements. The known UHM Ligand Motifs (ULMs) show a typical signature of a short positively charged run preceding a Trp-Asp pair (although the Asp is not always conserved.) ULM sequences with important functions in mRNA processing were found in the constitutive splicing factors U2AF65, SF1 and SAP155. The structure of the U2AF65-ULM reveals a larger induced fit module than the signature motif (1JMT) (Kielkopf,2001). It is recognized by the UHM in U2AF35 with low nanomolar affinity and mediates the heterodimerization of these two proteins, which is crucial for U2 snRNP recruitment in early splicing initiation. The SF1 ULM is used for recruitment to the branch point sequence by binding to the U2AF65-UHM (Selenko,2003). ATP-dependent rearrangements of the snRNPs cause the SF1-ULM to be replaced by ULMs in SAP155 later in the splicing process (Thickman,2006). Thus, the UHM-ULM interactions known so far all mediate essential interactions in the splicing process. The Rev proteins of HIV1, HIV2 and SIV have a highly conserved ULM mimic (Pabis,2019). The main cellular UHM-containing protein that binds to Rev is U2AF65. As well as being a constitutive splicing protein, U2AF65 is also involved in nuclear export of mRNAs. The ULM is directly involved in inhibition of splicing by Rev, switching on the late HIV gene expression which requires unspliced HIV mRNA. |
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
| Acc., Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | #Ev. | Organism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P17280 rev REV_SIVCZ |
42 | 47 | TRKARRNRRRRWRARQKQIS | TP | 1 | SIVcpz GAB1 | |
| P15830 rev REV_HV2D2 |
37 | 42 | TASQRRNRRRRWKRRGLQIL | TP | 1 | Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (ISOLATE D205,7) | |
| P04618 rev REV_HV1H2 |
41 | 46 | TRQARRNRRRRWRERQRQIH | TP | 6 | HIV-1 M:B_HXB2R | |
| P54253 ATXN1 ATX1_HUMAN |
770 | 775 | PSKPAATRKRRWSAPESRKL | TP | 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| O75533 SF3B1 SF3B1_HUMAN |
333 | 339 | PTPGASKRKSRWDETPASQM | TP | 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| O75533 SF3B1 SF3B1_HUMAN |
289 | 294 | GGATSSARKNRWDETPKTER | TP | 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| O75533 SF3B1 SF3B1_HUMAN |
195 | 201 | ASQPPSKRKRRWDQTADQTP | TP | 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| Q15637 SF1 SF01_HUMAN |
15 | 23 | LDFPSKKRKRSRWNQDTMEQ | TP | 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) |
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement