| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | EH ligand |
| Functional site description: | Asn-Pro-Phe motif responsible for the interaction with Eps15 homology (EH) domain. |
| ELM Description: | The canonical EH binding peptide is a strongly conserved NPF motif. The adjacent residues can affect affinity but are too poorly conserved to be modeled in the regular expression. |
| Pattern: | .NPF. |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0000586 |
| Present in taxons: | Eukaryota Homo sapiens Mus musculus |
| Interaction Domains: |
|
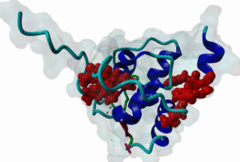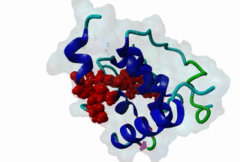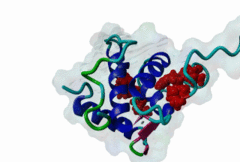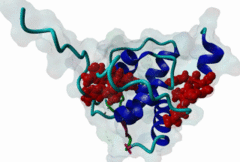
The EH (for Eps15 homology) domain is present in three copies in the amino terminus of the tyrosine kinase substrates Eps15 and Eps15R and shared with other proteins of mammals, flies, nematode, plants, yeast and possibly all other eukaryotes. EH domains are exclusively found in proteins that function in endocytosis and vesicular trafficking and are believed to regulate these processes. They recognize proteins containing single or multiple NPF (Asn-Pro-Phe) motifs, such as RAB, NUMB, SCAMP, Syndapin, Stonin2, CALM, synaptojanin and epsin. Some of the interactions between EH-domain containing proteins and NPF-containing proteins are known to regulate receptor-mediated endocytosis. EH domains consist of four helices: Helices 1 and 2 as well as 3 and 4 constitute helix-loop-helix motifs of the EF hand type. The pattern of amino acids defining EH domains consists of a central tryptophan residue situated on the third helix that is flanked by an array of highly conserved, mostly hydrophobic residues. These residues form a hydrophobic groove between helices 2 and 3 which accommodates the NPF motif of the binding partner. Measurements of EH interactions are often in the mid-micromolar range, somewhat lower affinity than most linear motifs. This suggests that co-operativity will be important to generate stable binding interactions. For the EH domains of Eps15 (more precisely the N-terminal and central EH domain) binding is enhanced when Thr or Ser occupy the two positions preceding NPF and when a hydrophobic or basic residue follows. Acidic residues in the flanking regions are mostly found in ligands of the family of EHD (EH domain containing) proteins, whereas they decrease the affinity of NPF ligands towards the EH domains of Eps15 or Intersectin. Some variations of the canonical binding mode have been reported. The EH domains of Reps, for example, have been reported to bind to DPF (Asp-Pro-Phe) motifs in addition to NPF motifs. Furthermore the EH domain of EHD2 has been shown to bind to an internal GPF (Gly-Pro-Phe) motif, which might constitute an autoinhibitory mechanism. An interaction between two adjacent NPF motifs, found within Stonin2, and a single EH domain of Eps15 was found to increase specificity and affinity dramatically. Given that NPF motifs as well as EH domains often occur in multiple copies within a single protein, co-operative, multivalent binding modes might be a general mechanism by which EH domains modulate their binding properties. |
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement