LIG_FHA_1
| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | FHA phosphopeptide ligands |
| Functional site description: | The FHA domain is a signal transduction module which recognizes phosphothreonine containing peptides on the ligand proteins. FHA domains partake in many signalling processes but are especially prevalent in nuclear proteins that are involved in cell cycle checkpoint, DNA repair and transcriptional regulation. |
| ELMs with same func. site: | LIG_FHA_1 LIG_FHA_2 |
| ELM Description: | LIG_FHA_1 motifs are short phosphothreonine modules binding FHA domains with large aliphatic amino acids at the pT+3 position. The motif has the consensus sequence of T..[IVL]. Proteins with FHA domains having this preference include the checkpoint kinase chk2 (Li,2002) and DNA repair protein rad9 (Byeon,2001). |
| Pattern: | ..(T)..[ILV]. |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0086622 |
| Present in taxon: | Eukaryota |
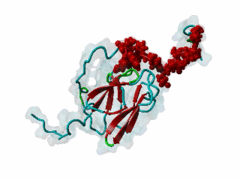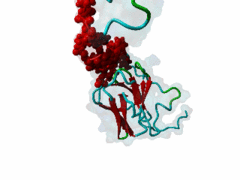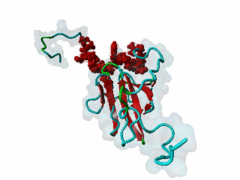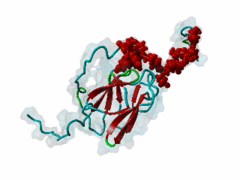
| Interaction Domain: |
FHA (PF00498)
FHA domain
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
The forkhead-associated FHA domain is a phosphopeptide-binding domain first identified in a group of forkhead transcription factors (Hofmann,1995). FHA are small domains (<100 amino acids) that form a sandwich of two anti-parallel beta sheets. They are present in a wide variety of proteins from both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (Li,2000). The existence of FHA domains in a wide variety of proteins means they are involved in diverse cellular functions including signal transduction and vesicular transport. In plants, FHA domains participate in the regulation of receptor-like protein kinase signalling pathways (Lee,2003). There are many nuclear FHA-domain containing proteins: these have a variety of roles involved in cell-cycle checkpoint control, DNA repair, signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, and pre-mRNA splicing. Some of the FHA domain-containing proteins are present in the plasma membrane. While FHAs bind to phosphothreonine motifs, BRCT domains recognize phosphoserine motifs in otherwise similar nuclear regulatory contexts. Although weak in vitro binding of phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine peptides has been observed, all high affinity interactions utilize phosphothreonine, which may be an essential requirement for the biological ligands. The optimal FHA domain binding sequence is a phosphothreonine peptide with pT+3 specificity. So far there are two well characterised motifs: TXX[ILV] and TXX[DE]. While TXXC and TXXA have been observed, they are not currently modeled in ELM. The TXXC linear motif forms part of a larger induced fit interaction with the FHA domain (Li,2000; Yongkiettrakul,2004; Lee,2003). More variations among the FHA-binding motifs are expected to be found. |
-
Interaction of a protein phosphatase with an Arabidopsis serine-threonine
receptor kinase.
Stone JM, Collinge MA, Smith RD, Horn MA, Walker JC
Science 1994 Nov 4; 266 (5186), 793-5
PMID: 7973632
-
DUN1 encodes a protein kinase that controls the DNA damage response in
yeast.
Zhou Z, Elledge SJ
Cell 1993 Dec 17; 75 (6), 1119-27
PMID: 8261511
-
Interaction of the maize and Arabidopsis kinase interaction domains with a
subset of receptor-like protein kinases: implications for transmembrane
signaling in plants.
Braun DM, Stone JM, Walker JC
Plant J 1997 Jul; 12 (1), 83-95
PMID: 9263453
-
A possible role for kinase-associated protein phosphatase in the
Arabidopsis CLAVATA1 signaling pathway.
Williams RW, Wilson JM, Meyerowitz EM
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997 Sep 16; 94 (19), 10467-72
PMID: 9294234
-
Rad53 FHA domain associated with phosphorylated Rad9 in the DNA damage
checkpoint.
Sun Z, Hsiao J, Fay DS, Stern DF
Science 1998 Jul 10; 281 (5374), 272-4
PMID: 9657725
-
The FHA domain is a modular phosphopeptide recognition motif.
Durocher D, Henckel J, Fersht AR, Jackson SP
Mol Cell 1999 Sep; 4 (3), 387-94
PMID: 10518219
-
NIPP1-mediated interaction of protein phosphatase-1 with CDC5L, a
regulator of pre-mRNA splicing and mitotic entry.
Boudrez A, Beullens M, Groenen P, Van Eynde A, Vulsteke V, Jagiello I, Murray M, Krainer AR, Stalmans W, Bollen M
J Biol Chem 2000 Aug 18; 275 (33), 25411-7
PMID: 10827081
-
The forkhead-associated domain of Ki-67 antigen interacts with the novel
kinesin-like protein Hklp2.
Sueishi M, Takagi M, Yoneda Y
J Biol Chem 2000 Sep 15; 275 (37), 28888-92
PMID: 10878014
-
II. Structure and specificity of the interaction between the FHA2 domain
of Rad53 and phosphotyrosyl peptides.
Wang P, Byeon IJ, Liao H, Beebe KD, Yongkiettrakul S, Pei D, Tsai MD
J Mol Biol 2000 Sep 29; 302 (4), 927-40
PMID: 10993733
-
The FHA domain mediates phosphoprotein interactions.
Li J, Lee GI, Van Doren SR, Walker JC
J Cell Sci 2000 Dec; 113, 4143-9
PMID: 11069759
-
The molecular basis of FHA domain:phosphopeptide binding specificity and
implications for phospho-dependent signaling mechanisms.
Durocher D, Taylor IA, Sarbassova D, Haire LF, Westcott SL, Jackson SP, Smerdon SJ, Yaffe MB
Mol Cell 2000 Nov; 6 (5), 1169-82
PMID: 11106755
-
Structure of the FHA1 domain of yeast Rad53 and identification of binding
sites for both FHA1 and its target protein Rad9.
Liao H, Yuan C, Su MI, Yongkiettrakul S, Qin D, Li H, Byeon IJ, Pei D, Tsai MD
J Mol Biol 2000 Dec 15; 304 (5), 941-51
PMID: 11124038
-
A novel nucleolar protein, NIFK, interacts with the forkhead associated
domain of Ki-67 antigen in mitosis.
Takagi M, Sueishi M, Saiwaki T, Kametaka A, Yoneda Y
J Biol Chem 2001 Jul 6; 276 (27), 25386-91
PMID: 11342549
-
Solution structure of the yeast Rad53 FHA2 complexed with a
phosphothreonine peptide pTXXL: comparison with the structures of
FHA2-pYXL and FHA1-pTXXD complexes.
Byeon IJ, Yongkiettrakul S, Tsai MD
J Mol Biol 2001 Nov 30; 314 (3), 577-88
PMID: 11846568
-
The FHA domain.
Durocher D, Jackson SP
FEBS Lett 2002 Feb 20; 513 (1), 58-66
PMID: 11911881
-
Structural and functional versatility of the FHA domain in DNA-damage
signaling by the tumor suppressor kinase Chk2.
Li J, Williams BL, Haire LF, Goldberg M, Wilker E, Durocher D, Yaffe MB, Jackson SP, Smerdon SJ
Mol Cell 2002 May; 9 (5), 1045-54
PMID: 12049740
-
Phosphorylation-dependent interaction between the splicing factors SAP155
and NIPP1.
Boudrez A, Beullens M, Waelkens E, Stalmans W, Bollen M
J Biol Chem 2002 Aug 30; 277 (35), 31834-41
PMID: 12105215
-
NMR structure of the forkhead-associated domain from the Arabidopsis
receptor kinase-associated protein phosphatase.
Lee GI, Ding Z, Walker JC, Van Doren SR
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003 Sep 30; 100 (20), 11261-6
PMID: 14500786
-
Mdt1, a novel Rad53 FHA1 domain-interacting protein, modulates DNA damage
tolerance and G(2)/M cell cycle progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Pike BL, Yongkiettrakul S, Tsai MD, Heierhorst J
Mol Cell Biol 2004 Apr; 24 (7), 2779-88
PMID: 15024067
-
The ligand specificity of yeast Rad53 FHA domains at the +3 position is
determined by nonconserved residues.
Yongkiettrakul S, Byeon IJ, Tsai MD
Biochemistry 2004 Apr 6; 43 (13), 3862-9
PMID: 15049693
-
PhosphoThr peptide binding globally rigidifies much of the FHA domain from
Arabidopsis receptor kinase-associated protein phosphatase.
Ding Z, Lee GI, Liang X, Gallazzi F, Arunima A, Van Doren SR
Biochemistry 2005 Aug 2; 44 (30), 10119-34
PMID: 16042389
-
Sequential phosphorylation and multisite interactions characterize
specific target recognition by the FHA domain of Ki67.
Byeon IJ, Li H, Song H, Gronenborn AM, Tsai MD
Nat Struct Mol Biol 2005 Nov; 12 (11), 987-93
PMID: 16244663
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
| Acc., Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | #Ev. | Organism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8NQJ3 odhI ODHI_CORGL |
12 | 18 | GTPEPQVETTSVFRADLLKE | TP | 7 | Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 | |
| P9WJA9 garA GARA_MYCTU |
19 | 25 | TSDEVTVETTSVFRADFLSE | TP | 2 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | |
| P34217 PIN4 PIN4_YEAST |
303 | 309 | QLDFNDPDTLEIYSQLLLFK | TP | 5 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker"s yeast) | |
| P14737 RAD9 RAD9_YEAST |
601 | 607 | TIMSEVELTQELPEVEEQQD | TP | 2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker"s yeast) | |
| Q9SYQ8 CLV1 CLV1_ARATH |
866 | 872 | YIAPEYAYTLKVDEKSDVYS | TP | 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress) | |
| O96017 CHEK2 CHK2_HUMAN |
66 | 72 | LSSLETVSTQELYSIPEDQE | TP | 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) |
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement